Publication | Biting the hand that feeds: Anthropogenic drivers interactively make mosquitoes thrive
This publication is part of the project ‘Preparing for vector-borne virus outbreaks in a changing world: a One Health Approach’ (NWA.1160.1S.210) which is (partly) financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO).

Authors: S.P. Boerlijst, E.S.Johnston, A.Ummels, L.Krol, E.Boelee, P.M.van Bodegom, M.J.J.Schrama.
Highlights
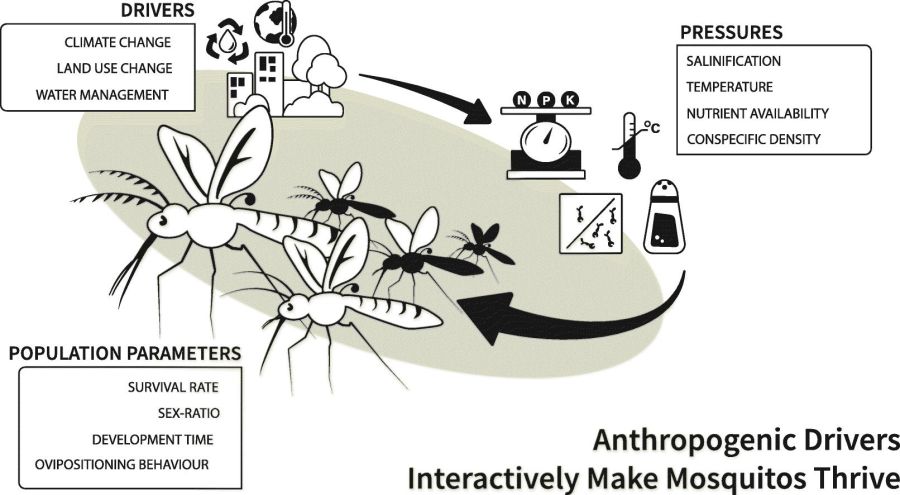
- Impacts of interlinked anthropogenic stressors are relatively unknown.
- Such stressors include land use change, freshwater pollution, and extreme weather.
- Full-factorial experiments assessed stressor impacts on disease vector Culex pipiens.
- The stressors and their interactions had major impacts on key mosquito life-history traits.
- Results show important ramifications for mosquito populations and the pathogenic landscape.
Abstract
Anthropogenic stressors on the environment are increasing at unprecedented rates and include urbanization, nutrient pollution, water management, altered land use and climate change. Their effects on disease vectors are poorly understood. A series of full factorial experiments investigated how key human induced abiotic pressures, and interactions between these, affect population parameters of the cosmopolitan disease vector, Culex pipiens s.l. Selected pressures include eutrophication, salinity, mean temperature, and temperature fluctuation. Data were collected for each individual pressure and for potential interactions between eutrophication, salinization and temperature. All experiments assessed survival, time to pupation, time to emergence, sex-ratio and ovipositioning behavior. The results show that stressors affect vector survival, may speed up development and alter female to male ratio, although large differences between stressors exist to quite different extents. While positive effects of increasing levels of eutrophication on survival were consistent, negative effects of salinity on survival were only apparent at higher temperatures, thus indicating a strong interaction effect between salinization and temperature. Temperature had no independent effect on larval survival. Overall, increasing eutrophication and temperatures, and the fluctuations thereof, lowered development rate, time to pupation and time to emergence while increasing levels of salinity increased development time. Higher levels of eutrophication positively impacted egg-laying behavior; the reverse was found for salinity while no effects of temperature on egg-laying behavior were observed. Results suggest large and positive impacts of anthropogenically induced habitat alterations on mosquito population dynamics. Many of these effects are exacerbated by increasing temperatures and fluctuations therein. In a world where eutrophication and salinization are increasingly abundant, mosquitoes are likely important benefactors. Ultimately, this study illustrates the importance of including multiple and combined stressors in predictive models as well as in prevention and mitigation strategies, particularly because they resonate with possible, but yet underdeveloped action plans.
Source: ScienceDirect
Date: november 21th 2022